10 Ruby on Rails Best Practices
Bài đăng này đã không được cập nhật trong 4 năm

Ruby on Rails là một web framework được viết bằng ngôn ngữ lập trình Ruby. Nhưng sự khác biệt là nó có rất nhiều công cụ giúp tăng tốc quá trình phát triển và làm cho công việc được dễ dàng hơn. cho phép chúng ta tập trung vào nhiệm vụ chứ không phải là công nghệ. Nhưng để làm việc tốt với Rails đặc biệt đối với người mới bắt đầu là rất quan trọng. Trong bài viết này mình sẽ giới thiệu về môt số best practices in Ruby on Rails.
1. Tow Space Indentation
Đây là một trong những hướng dẫn phong cách thích nghi rộng rãi nhất và thoả thuận trong cộng đồng Ruby. Sử dụng 2 thụt vào không gian thay vì 4 không gian thụt đầu dòng. Chúng ta hãy xem một ví dụ:
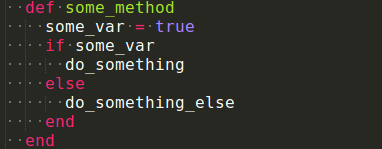
2. Define Predicate Methods with a ?
Trong Ruby, chúng ta có một quy ước cho các phương thức trả về giá trị true or false kết thúc bằng dấu ?. Trong một số ngôn ngữ bạn sẽ thấy phương thức hoạc các tên biến được định nghĩa như is_valid or is_paid, etc. Ruby không khuyến khích phong cách này và nó theo một cách ngôn ngữ của con người giống như object.valid? or fee.paid? (chú ý không dùng tiền tố is_).
3. Iteration: Use each Instead of for
Hầu như tất cả các lập trình viên của Ruby sẻ dụng each thay vì for.
for
for i in 1..100
...
end
each
(1..100).each do |i|
...
end
4. Conditionals: Use unless Instead of !if
Bad
if !true
do_this
end
or
if name != "sarmad"
do_that
end
Good
unless true
do_this
end
or
unless name == "sarmad"
do_that
end
Bad
unless user.save
throw error
else
return success
end
Good
if user.save
return success
else
throw error
end
5. Short Circuits**
Trong 1 số ngôn ngữ lập trình, biểu thức logic thường có tính đoản mạch (Short-circuit). hãy xem ví dụ này:
if user.gender == "male" && user.age > 17
do_something
elsif user.gender == "male" && user.age < 17 && user.age > 5
do_something_else
elsif user.age < 5
raise StandardError
end
Trong trường hợp này, nó cần phải kiểm tra tất cả các điều kiện để tìm user dưới 5 tuổi và raise một exception. Cách tốt hơn là:
raise StandardError if user.age < 5
if user.gender == "male" && user.age > 17
do_something
elsif user.gender == "male" && user.age < 17 #we saved a redundant check here
do_something_else
end
=> Nó là hiệu quả hơn để return sớm.
6. DRY (Don’t Repeat Yourself)
Khi viết code bạn suy nghĩ cách tối ưu nhất để đảm bảo rằng bạn Don’t Repeat Yourself, Trách sự trùng lặp nhiều. Hãy xem qua ví dụ này:
class Mercedes
def accelerate
"60MPH in 5 seconds"
end
def apply_brakes
"stopped in 4 seconds"
end
def open_boot
"opened"
end
def turn_headlights_on
"turned on"
end
def turn_headlights_off
"turned off"
end
end
class Audi
def accelerate
"60MPH in 6.5 seconds"
end
def apply_brakes
"stopped in 3.5 seconds"
end
def open_boot
"opened"
end
def turn_headlights_on
"turned on"
end
def turn_headlights_off
"turned off"
end
end
Chúng ta có 3 methods trùng lặp, open_boot, turn_headlights_on, và turn_headlights_off. Để giải quyết vấn đề DRY chúng ta hãy sử dụng class inheritance and/or abstract classes. Chúng ta viết lại:
class Car
def open_boot
"opened"
end
def turn_headlights_on
"turned on"
end
def turn_headlights_off
"turned off"
end
end
class Mercedes < Car
def accelerate
"60MPH in 5 seconds"
end
def apply_brakes
"stopped in 4 seconds"
end
end
class Audi < Car
def accelerate
"60MPH in 6.5 seconds"
end
def apply_brakes
"stopped in 3.5 seconds"
end
end
7. Smart Use of Enums
Enum là kiểu dữ liệu liệt kê, giúp bạn tổ chức dữ liệu khoa học hơn, code được trong sáng dễ hiểu hơn. Ta có một ví dụ: Giả sử bạn một model là Book và có column status để lưu trữ các status (draft, completed, published).
if book.status == "draft"
do_something
elsif book.status == "completed"
do_something
elsif book.status == "published"
do_something
end
or
if book.status == 0 #draft
do_something
elsif book.status == 1 #completed
do_something
elsif book.status == 2 #published
do_something
end
=> ở đây bạn nên dùng Enums. define column status là integer (not null) và tạo một giá trị default mà bạn muốn.( after_create). Bây giờ, bạn define một enums trong model Book như thế này:
enum status: { draft: 0, completed: 1, published: 2 }
Và bạn có thể viết lại đoạn code trên:
if book.draft?
do_something
elsif book.completed?
do_something
elsif book.published?
do_something
end
Giờ code của bạn trông thật rõ ràng phải không nào. Ngoài ra nó cũng còn cung cấp cho bạn những phương pháp để update status.
book.draft!
book.completed!
book.published!
8. Fat Models, Skinny Controllers and Concerns
ROR áp dụng kiến trúc MVC để xây dựng framework. Nên để làm việc hiểu quả chúng ta cần phải hiêu về MVC và cách làm việc hiệu quả với MVC. Một ví dụ cho chúng ta thấy về MVC.
class BooksController < ApplicationController
before_action :set_book, only: [:show, :edit, :update, :destroy, :publish]
code omitted for brevity
def publish
@book.published = true
pub_date = params[:publish_date]
if pub_date
@book.published_at = pub_date
else
@book.published_at = Time.zone.now
end
if @book.save
success response, some redirect with a flash notice
else
failure response, some redirect with a flash alert
end
end
code omitted for brevity
private
Use callbacks to share common setup or constraints between actions
def set_book
@book = Book.find(params[:id])
end
code omitted for brevity
end
Nếu như chúng ta xử lý các logic của model ở controller là không hợp lý. chúng ta move các logic này vào trong model.
class Book < ActiveRecord::Base
def publish(publish_date)
self.published = true
if publish_date
self.published_at = publish_date
else
self.published_at = Time.zone.now
end
save
end
end
class BooksController < ApplicationController
before_action :set_book, only: [:show, :edit, :update, :destroy, :publish]
code omitted for brevity
def publish
pub_date = params[:publish_date]
if @book.publish(pub_date)
success response, some redirect with a flash notice
else
failure response, some redirect with a flash alert
end
end
code omitted for brevity
private
Use callbacks to share common setup or constraints between actions
def set_book
@book = Book.find(params[:id])
end
code omitted for brevity
end
Fat model - Skinny controller: Hiện tại, Controller đang làm việc điều khiển, chuyển hướng, nên các thao tác tương tác db sẽ được đưa vào Model. Ta không thể để Controller xử lý các thao tác db, vậy nên, càng ngày, Model sẽ càng phình ra (Fat model), còn Controller thì chỉ có mấy dòng (Thin controller).
Xử lý logic trong view Ở trong view nếu chỉ có một ít logic đơn giản thì tạm chấp nhận được, nhưng nếu logic phức tạp quá thì thật sự không ổn.
9. Nested Resources/Routes
Sử dụng routes lồng nhau (nested routes) để thể hiện mối quan hệ của các model trong ActiveRecord. Ví dụ bạn có mô hình:
Post model has many comments Comment model belongs to Post Và trong config/routes.rb
resources :posts
resources :comments
- http://localhost:3000/posts
- http://localhost:3000/posts/1
- http://localhost:3000/posts/1/edit
- http://localhost:3000/comments
- http://localhost:3000/comments/1
- http://localhost:3000/comments/1/edit
Nó ok, nhưng không phải là cách tốt. Chúng ta cần sử dụng nested routes Comment lồng bên trong Post. Đây là cách làm:
resources :posts do
resources :comments
end
- http://localhost:3000/posts
- http://localhost:3000/posts/1
- http://localhost:3000/posts/1/edit
- http://localhost:3000/posts/1/comments
- http://localhost:3000/posts/1/comments/1
- http://localhost:3000/posts/1/comments/1/edit
10. Don’t Put Too Much Logic in Views
Views là the presentation layer, không nên chưa logic. Bạn nên tránh việc kiểm tra như thế này:
<% if book.published? && book.published_at > 1.weeks.ago %>
<span>Recently added</span>
<% end %>
//or
<% if current_user.roles.collect(&:name).include?("admin") || (user == book.owner && book.draft?) %>
<%= link_to 'Delete', book, method: :delete, data: { confirm: 'Are you sure?' } %>
<% end %>
Bạn có thể di chuyển kiểm tra điều kiện này vào module helper(app/helpers). ví dụ:
app/view/helpers/application_helper.rb
module ApplicationHelper
def recently_added?(book)
book.published? && book.published_at > 1.weeks.ago
end
current_user is defined in application controller, which can be
accessed from helper modules & methods
def can_delete?(book)
current_user.roles.collect(&:name).include?("admin") || (user == book.owner && book.draft?)
end
end
edit code view trên như sau:
<% if recently_added?(book) %>
<span>Recently added</span>
<% end %>
//and
<% if can_delete?(book) %>
<%= link_to 'Delete', book, method: :delete, data: { confirm: 'Are you sure?' } %>
<% end %>
Kết Luận
Đây là một sỗ Best practices của Rails. Hi vọng nó sẽ giúp được cho các bạn mới bắt đầu để làm việc tốt hơn với Rails.
Tham khảo https://www.sitepoint.com/10-ruby-on-rails-best-practices-3/
All rights reserved