Intergrate Redis on Rails
Bài đăng này đã không được cập nhật trong 4 năm
Today, I am going to talk about Redis which is the most popular technology for storing web data especially cache data. In this artcle, I'll show you how to intergrate redis to our Rails app, and how we can use in our app.
But first we need to know what is Redis? Why do we use Redis? How can we set it up?
What\why\how is Redis?
Redis is a NoSQL database which store data in memory. However, according to the redis official web site:
Redis is an open source (BSD licensed), in-memory data structure store, used as database, cache and message broker. It supports data structures such as strings, hashes, lists, sets, sorted sets with range queries, bitmaps, hyperloglogs and geospatial indexes with radius queries.
Redis is fast because it is an in-memory key-value store so that the data retrieval is almost instantaneous & when we're using it to store cached data.
However, you'll need to get it installed in your computer first and you can install it base on your OS.
- For mac users:
$ brew install redis - For debian users:
$ sudo apt-get install redis
And to start redis server: $ redis-server and you are good to go.

Set up Redis on rails
Set up redis on rails is easy, and you can add it by this follow step:
- Add redis gem
gem 'redis' - run
$bundle install - add redis in initialization
config/initializers/redis.rband use it globally
#config/initializers/redis.rb
$redis = Redis.new(:host => 'localhost', :port => 6379)
however, you also can init redis on whenever you want to it instead of init it globally.
Demostration of using Redis on Rails
To demo the usage of redis, I am going to use my previous project plantlover source code which it is continue from article Image manipulation with Carrierwave and MiniMagick.
As my previous artcile, we have implemented the place where user able to view list of plants and it details infomation. So in the artcile we'll add one more feature which allow login user be able to create, update, and delete plants infomation. And we use redis to store the token data.
Lets create redis class in lib folder name plant_lover_redis.rb instead of use redis directly in application.
#lib/plant_lover_redis.rb
class PlantLoverRedis
NAMESPACE = 'plants_lover:'
class << self
def set(key, value)
$redis.set("#{NAMESPACE}#{key}", value)
expire(key)
end
def get(key)
$redis.get("#{NAMESPACE}#{key}")
end
def delete(key)
return false unless exist?(key)
$redis.del("#{NAMESPACE}#{key}")
true
end
def exist?(key)
$redis.exists("plants_lover:#{key}")
end
private
def expire(key)
$redis.expire("#{NAMESPACE}#{key}", 1.hour)
end
end
end
let's create user model $rails g model name:string username:string password_digest:string, and add has_secure_password into user model. However, you need to enable gem 'bcrypt' in order to use this feature.
#app/model/user.rb
class User < ActiveRecord::Base
validates :name, :username, presence: true,
length: { minimum: 2, maximum: 40 }
validates :username, uniqueness: true
has_secure_password
# override to_json for
def to_json(options={})
options[:except] ||= [:password_digest]
super(options)
end
end
let's seed sample of user in to database:
...
User.create! name: "RathanakJame",
username: "rathanak",
password: '1234567890',
password_confirmation: '1234567890',
sex: 'M'
10.times do |n|
User.create! name: "Rathanak-#{n}",
username: "rathanak_#{n}",
password: '1234567890',
password_confirmation: '1234567890',
sex: 'M'
end
...
here we create sessions_controller for user signin and signout.
in this controller we have two action signin which use SecureRandom.base64 to generate token key than PlantLoverRedis.set(token, user.id) save token as key to redis and respond the token key to user when use loggin successfully, and signout will PlantLoverRedis.delete(token) remove token from redis store.
#app/controllers/sessions_controller.rb
class SessionsController < ApplicationController
def create
username = params[:username]
user_password = params[:password]
user = User.find_by(username: username)
if user && user.authenticate(user_password)
token = SecureRandom.base64
loop do
break unless PlantLoverRedis.exist?(token)
token = SecureRandom.base64
end
PlantLoverRedis.set(token, user.id)
render json: { message: 'login success ', data: token}, status: 200
else
render json: { errors: 'Invalid username or password'}, status: 422
end
end
def destroy
token = request.headers['HTTP_PLANLOVERTOKEN']
PlantLoverRedis.delete(token)
render json: { message: 'sign out successfully'}, status: 200
end
end
let's try signin:
$curl -X POST -d '{"username": "rathanak", "password": "1234567890"}' -H 'Content-Type: application/json' http://localhost:3000/signin -w '\n'
and here we got

let's try signout
$curl localhost:3000/signout -H 'PlanLoverToken: UE1umYo+8KftmKPQ2prU+A==' -w '\n'
and here we got:

Lets' authenticate and authorize user that perform action on our
plants_controller.rb.
#app/controllers/plants.rb
class PlantsController < ApplicationController
before_filter :authenticate_with_token, except: [:show, :index]
before_action :set_plant, only: [:show, :edit, :update, :destroy]
before_action :authorize_action, only: [:edit, :update, :destroy]
....
....
private
...
def set_plant
@plant = Plant.find(params[:id])
end
def authorize_action
unless @user && @plant
render json: { errors: 'there not user or plants!'}, status: :unauthorized
end
if @plant.user.id != @user.id
render json: { errors: 'user is not authorized on this action'}, status: :unauthorized
end
end
def authenticate_with_token
token = request.headers['HTTP_PLANLOVERTOKEN']
if PlantLoverRedis.exist?(token)
@user = User.find(PlantLoverRedis.get(token))
else
render json: { errors: 'Not authenticated!'}, status: :unauthorized
end
end
end
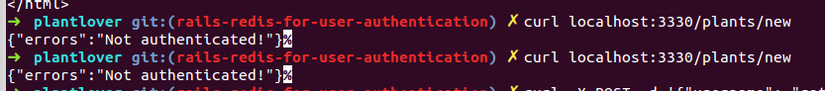
Access to plants controller without header
curl localhost:3330/plants/new
and here we got
than let's access with invalid and valid token key which we get from signin respond
$curl -X POST -d '{"username": "rathanak", "password": "1234567890"}' -H 'Content-Type: application/json' http://localhost:3330/signin
$curl localhost:3330/plants/new -H 'PlanLoverToken: INVALIA TOKEN'
$curl localhost:3330/plants/new -H 'PlanLoverToken: VALID TOKEN'
and here we got

Now try with unauthorized user
$curl -X PATCH -d '{"name": "Red flower", "description": "this is the red florwer"}' -H 'PlanLoverToken: KzxuBRlu2aprBa4g10LZHw==' -H 'Content-Type: application/json' http://localhost:3330/plants/3
here what we got

yaya, It works. 
Resources
Next Step
In this article, we just introduce you to Redis and how can we intergrate its functionality with our Rails app. However, you can do many more with Redis and the good place which you can explore is on its official web site.
All rights reserved