Directive trong AngularJS
Bài đăng này đã không được cập nhật trong 5 năm
Chào các bạn, bài viết này mình sẽ trình bày về directive - một khái niệm quen thuộc trong AngularJS.
Angular Directive là gì?
Directive là một khái niệm trong Angular Framework, nó là những thành phần mở rộng cho các thẻ html dùng bổ trợ các thuộc tính nâng cao cho các thẻ html.
Với directive, Angular compiler sẽ render ra html mà trình duyệt hiểu được dựa vào attribute html, từ comment hay từ một tag bất kỳ nào được đặt trên trang ...
Ví dụ chúng ta có một thẻ tag ảo:
<error-message></error-message>
Trình duyệt không thể hiểu thẻ error-message này, nhưng khi ứng dụng chạy, trình biên dịch (AngularJS $compiler) sẽ dựa trên chỉ dẫn của directive để convert thẻ tag ảo này thành thẻ mà trình duyệt có thể hiểu được.
Đó là một trong những cách mà directive làm việc. Bài viết này chúng ta cùng tìm hiểu xem directive là gì, nó hoạt động như thế nào, cách sử dụng directive và các loại directive nhé.
Như mình vừa ví dụ về một thẻ tag ảo: <error-message></error-message>, thẻ này là một directive Element, trình duyệt không thể đọc được thẻ này (trình duyệt chỉ có thể hiểu các thẻ html trong danh sách này), khi file html này được render, AngularJS thông qua directive được khai báo sẽ render thẻ này thành thẻ mà trình duyệt đọc được:
Trong AngularJS, chúng ta thường sử dụng các directive phổ biến và không thể thiếu: Ví dụ:
<input ng-model="modelName">
ng-model là một directive mặc định mà Angular cung cấp, nó là một directive A (attribute), dùng để gán các giá trị của các thẻ html trong form như input, select, radio, text-area....
Ngoài ra còn rất nhiều các directive được định nghĩa sẵn trong AngularJS như ng-controller, ng-bind, ng-init, ng-click, ng-show, ng-hide ... Chúng đều là directive, qua đó thấy rằng directive là một khái niệm rất quen thuộc trong Angular.
Directive hoạt động như thế nào
Các ví dụ sau đây sẽ là các custom directive do chúng ta tự định nghĩa để tìm hiểu cách khai báo và sử dụng luôn nhé.
Cùng xem ví dụ sau về Directive E (Element) để thấy cách hoạt động của một directive:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>AngularJS Directive</title>
<script src="https://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/angularjs/1.7.2/angular.min.js"></script>
<script src="directive-e-example.js"></script>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css">
</head>
<body>
<div ng-app="myApp" ng-controller="myCtrl">
<h3>Directive E (Element):</h3>
<error-notice></error-notice>
</div>
</body>
</html>
directive-e-example.js:
var app = angular.module("myApp", []);
app.directive("errorNotice", function() {
return {
restrict : "E",
template : "<p class='error-notice'>Has erorrs</p>"
};
});
Cú pháp khai báo: angular.module("myApp", []).directive(...)
Tên directive tuân theo quy tắc camelCase, ở html thẻ 'error-notice' thì tên directive cần khai báo là 'errorNotice'.
restrict: "E"
Khai báo loại directive thông qua cú pháp restrict, E là viết tắt của Element.
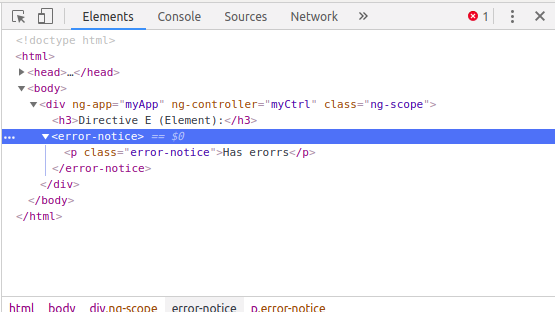
Angular sẽ render directive này như sau:
Các loại directive
Angular directive gồm có 5 loại:
- Directive E (element)
- Directive A (attribute)
- Directive C (class)
- Directive M (comment)
- Directive render qua file html
Directive E mình đã trình bày qua ví dụ vừa rồi, tiếp theo hãy xem các ví dụ của các directive còn lại để tìm hiểu xem nó khác gì với directive E nhé:
Directive A (attribute)
Như chúng ta biết thì mọi thẻ html đều có thể có attribute truyền vào để cung cấp thêm nhiều thông tin hơn cho một element, dạng attribute="value"
Như từ viết tắt của directive, angularJS sẽ thông qua attribute trong một thẻ html để nhận biết một directive.
Ví dụ:
<div error-attribute></div>
directive-a-example.js
var app = angular.module("myApp", []);
app.directive("errorAttribute", function() {
return {
restrict : "A",
template : "<p class='error-notice'>Has erorrs</p>"
};
});
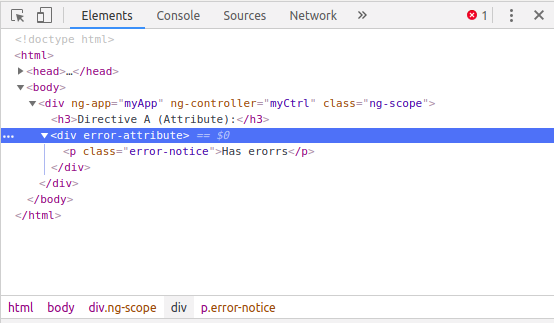
AngularJS compile đã render directive này như sau:
Directive C (class)
Với directive này, Angular sẽ dựa theo class để nhận biêt một directive.
<div class="has-error"></div>
var app = angular.module("myApp", []);
app.directive("hasError", function() {
return {
restrict : "C",
template : "<p class="error-notice">Something Error!</h1>"
};
});
Directive M (comment)
Code thường có comment để người viết có thể ghi chú/ giải thích về code ... Trong html thì comment có dạng sau:
<!–– đoạn comment ––>
Các đoạn comment này bạn phải inspect code lên để thấy. AngularJS hỗ trợ chúng ta khai báo directive trong comment, sau đây là ví dụ:
<!-- directive: commented-directive -->
var app = angular.module("myApp", []);
app.directive("commentDirective", function() {
return {
restrict : "M",
replace : true,
template : "<h1>Directive comment type!</h1>"
};
});
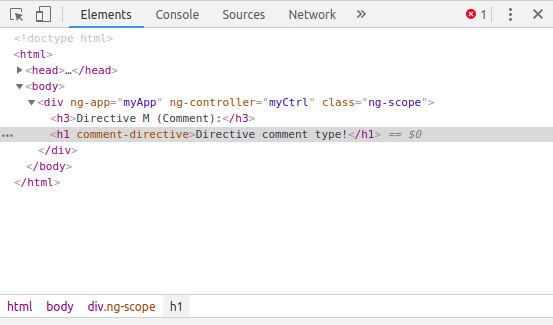
Và AngularJS đã render nó như sau, chúng ta không thấy luôn đoạn comment mà chỉ thấy content bên trong của directive:
Directive với templateUrl
Với những directive cần render nội dung dài thì rõ ràng không nên render ngay trong file js bởi nó sẽ khiến code trở nên cồng kềnh. Đối với trường hợp này thì chúng ta có thể sử dụng templateUrl, nội dung html sẽ viết ở một file html riêng, và thay vì dùng template thì sử dụng templateUrl:
Vì chạy html file thông thường AngularJS sẽ không render được file template external, mình chạy file này bằng http-server:
Các bạn có thể cài đặt Nodejs sau đó cài http-server:
sudo apt install nodejs npm
sudo npm install http-server -g
Sau đó gõ http-server ở thư mục code để chạy file html ở localhost.
Cùng xem cách khai báo của directive dùng templateUrl:
templateUrl : "/path/to/template.html"
Diretive này mình sẽ ví dụ render danh sách users
File list.html:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>AngularJS Directive</title>
<script src="https://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/angularjs/1.7.2/angular.min.js"></script>
<script src="users-controller.js"></script>
<script src="users-list-directive.js"></script>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="style.css">
</head>
<body>
<div ng-app="myApp">
<div ng-controller="usersController as vm">
<h2>Custom Directive with templateUrl</h2>
<!–– truyền list users vào directive này ––>
<users-list users="vm.users" title="My Lovers"/>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
user-list-template.html:
<div class="my-user-list">
<h1>{{title}}</h1>
<div ng-repeat="user in users">
<p><span ng-bind="user.name"></span>, <span ng-bind="user.age"></span> tuổi</p>
</div>
</div>
users-controller.js
var app = angular.module("myApp", []);
var ctrl = app.controller("usersController", function($scope) {
var vm = this;
vm.users = [
{name: 'Quyen', age: "22"},
{name: 'Hoai', age: "19"},
{name: 'Tham', age: "18"}
];
});
và cuối cùng khai báo directive, file users-list-directive.js:
app.directive("usersList", function() {
return {
restrict : "E",
templateUrl : "users-list-template.html",
scope: {
users: '=',
title: '@'
}
};
});
Note:
- scope: vùng này để khai báo các variable các bạn dùng trong directive, cả ở template
- Về binding attributes trong angular, ở directive này mình dùng '=' cho Object two way binding và '@' cho String value. Các bạn có thể tìm hiểu thêm về binding attribute trong angular ở link này
Như vậy mình vừa trình bày về directive trong AngularJS, hy vọng bài viết sẽ giúp ích cho những ai đang tìm hiểu về AngularJS directive. Nếu có thắc mắc gì thì hãy để lại comment thảo luận nhé.
All rights reserved