Eloquent Relationships Cheat Sheet - Cách khai báo & sử dụng Relationships trong Eloquent Laravel
Bài đăng này đã không được cập nhật trong 3 năm

One to One Relationship
Details:
Trong ví dụ, chúng ta có 2 model (Owner & Car), và 2 bảng (owners & cars).
Business Rules:
- Người lái xe - Owner chỉ có thể lái được 1 chiếc ô tô - Car.
- Chiếc ô tô - Car chỉ có thể được lái bởi người lái xe - Owner.
Relations Diagrams:
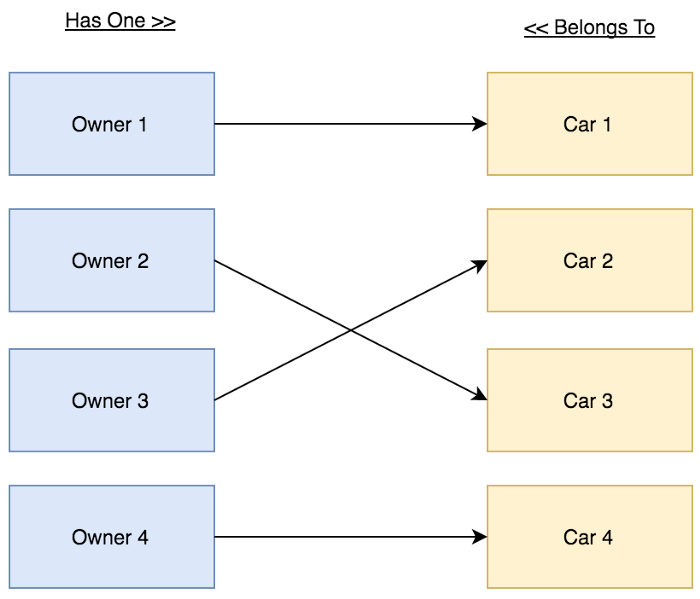
Relationship Details:
Trong bảng cars phải lưu trữ ID Owner (owner_id ).
Eloquent Models:
class Owner
{
public function car()
{
return $this->hasOne(Car::class);
}
}
class Car
{
public function owner()
{
return $this->belongsTo(Owner::class);
}
}
Database Migrations:
Schema::create('owners', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->string('name');
});
Schema::create('cars', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->string('name');
$table->integer('owner_id')->unsigned()->index()->nullable();
$table->foreign('owner_id')->references('id')->on('owners');
});
Store Records:
// Create relation between Owner and Car
$owner->car()->save($car);
// Create relation between Car and Owner
$car->owner()->associate($owner)->save();
Retrieve Records:
// Get Owner Car
$owner->car;
// Get Car Owner
$car->owner;
One to Many Relationship
Details:
Trong ví dụ, chúng ta có 2 model (Thief & Car), và 2 bảng (thieves & cars).
Business Rules:
- Tên trộm - Thief có thể trộm nhiều chiếc ô tô - Cars.
- Chiếc xe ô tô - Car có thể bị đánh cắp bởi 1 tên trộm - Thief.
Relations Diagrams:
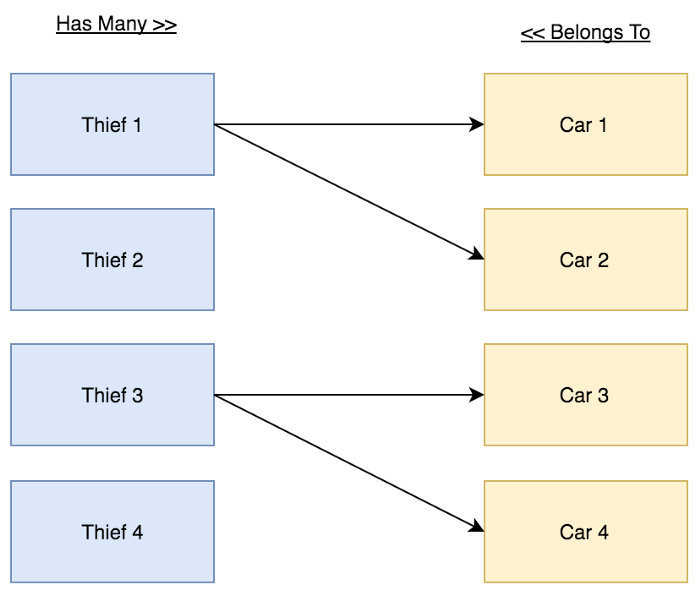
Relationship Details:
Trong bảng cars phải lưu trữ ID Thief (thief_id ).
Eloquent Models:
class Thief
{
public function cars()
{
return $this->hasMany(Car::class);
}
}
class Car
{
public function thief()
{
return $this->belongsTo(Thief::class);
}
}
Database Migrations:
Schema::create('thieves', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->string('name');
});
Schema::create('cars', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->string('name');
$table->integer('thief_id')->unsigned()->index()->nullable();
$table->foreign('thief_id')->references('id')->on('thieves');
});
Store Records:
// Create relation between Thief and Car.
$thief->cars()->saveMany([
$car1,
$car2,
]);
// Or use the save() function for single model.
$thief->cars()->save($car);
// Create relation between Car and Thief.
$car->thief()->associate($thief)->save();
Retrieve Records:
// Get Thief Car
$thief->cars;
// Get Car Thief
$car->thief;
Polymorphic One to Many Relationship
Details:
Trong ví dụ, chúng ta có 3 model (Man, Woman & Car), và 3 bảng (men, woman & cars).
Business Rules:
- 1 người con trai - Man (buyer) có thể mua được nhiều chiếc ô tô - Cars.
- 1 người con gái - Woman (buyer) có thể mua được nhiều chiếc ô tô - Cars.
- 1 chiếc ô tô - Car có thể được mua bởi 1 người mua nào đó (Người con trai - Man hoặc Người con gái - Woman).
Relations Diagrams:
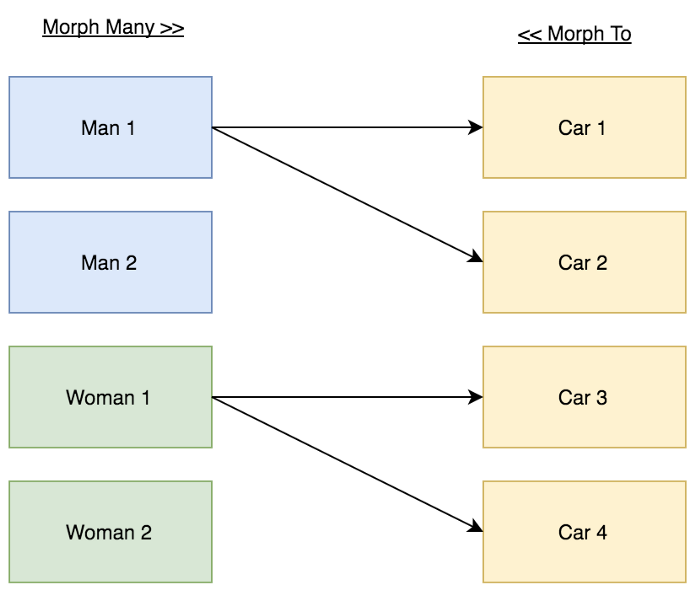
Relationship Details:
Trong bảng cars phải lưu trữ ID của người mua (buyer_id) và người mua đó là ai - người con trai hay người con gái (buyer_type)
Eloquent Models:
class Man
{
public function cars()
{
return $this->morphMany(Car::class, 'buyer');
}
}
class Woman
{
public function cars()
{
return $this->morphMany(Car::class, 'buyer');
}
}
class Car
{
public function buyer()
{
return $this->morphTo();
}
}
Database Migrations:
Schema::create('man', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->string('name');
});
Schema::create('woman', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->string('name');
});
Schema::create('cars', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->string('name');
$table->integer('buyer_id')->unsigned()->index()->nullable();
$table->string('buyer_type')->nullable();
// or use $table->morphs(‘buyer’); instead of "buyer_id" and "buyer_type"
});
Store Records:
// Create relation between buyer (Man/Woman) and Car.
$man->cars()->saveMany([
$car1,
$car2,
]);
$woman->cars()->saveMany([
$car1,
$car2,
]);
// Or use the save() function for single model.
$man->cars()->save($car);
$woman->cars()->save($car);
// Create relation between Car and buyer (Men/Women).
$car1->buyer()->associate($man)->save();
$car2->buyer()->associate($woman)->save();
Retrieve Records:
// Get buyer (Man/Woman) Cars
$man->cars
$woman->cars
// Get Car buyer (Man and Woman)
$car->buyer
Many to Many Relationship
Details:
Trong ví dụ, chúng ta có 2 model (Driver & Car), 2 bảng (drivers & cars), và 1 bảng trung gian - pivot (car_driver).
Business Rules:
- 1 người lái xe - Driver có thể lái được nhiều loại xe ô tô khác nhau - Cars.
- 1 chiếc xe ô tô - Car có thể được điều khiển bởi nhiều người lái xe - Drivers.
Relations Diagrams:
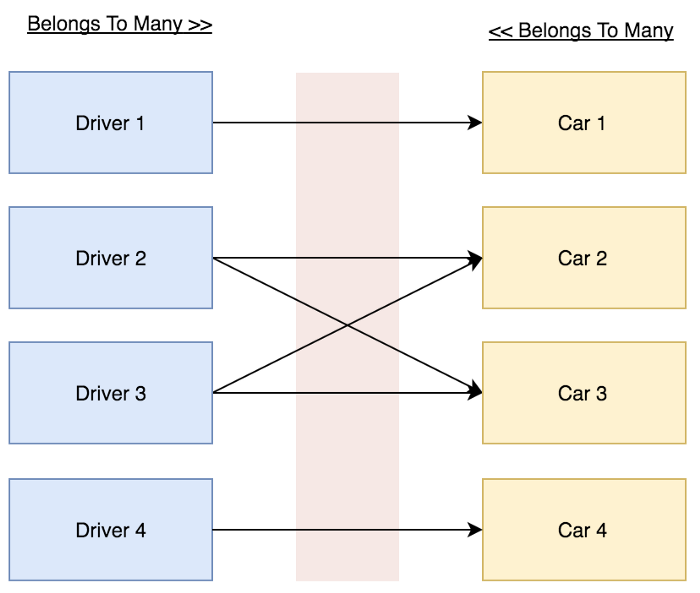
Relationship Details:
Bảng trung gian - Pivot (car_driver) phải lưu ID người lái xe (driver_id) và ID chiếc xe ô tô mà người lái xe lái (car_id).
Eloquent Models:
class Driver
{
public function cars()
{
return $this->belongsToMany(Car::class);
}
}
class Car
{
public function drivers()
{
return $this->belongsToMany(Driver::class);
}
}
Database Migrations:
Schema::create('drivers', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->string('name');
});
Schema::create('cars', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->string('name');
});
Schema::create('car_driver', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->integer('car_id')->unsigned()->index();
$table->foreign('car_id')->references('id')->on('cars')->onDelete('cascade');
$table->integer('driver_id')->unsigned()->index();
$table->foreign('driver_id')->references('id')->on('drivers')->onDelete('cascade');
});
Store Records:
// Create relation between Driver and Car.
$driver->cars()->attach([
$car1->id,
$car2->id,
]);
// Or use the sync() function to prevent duplicated relations.
$driver->cars()->sync([
$car1->id,
$car2->id,
]);
// Create relation between Car and Driver.
$car->drivers()->attach([
$driver1->id,
$driver2->id,
]);
// Or use the sync() function to prevent duplicated relations.
$car->drivers()->sync([
$driver1->id,
$driver2->id,
]);
Retrieve Records:
// Get Driver Car
$driver->cars
// Get Car Drivers
$car->drivers
Polymorphic Many to Many Relationship
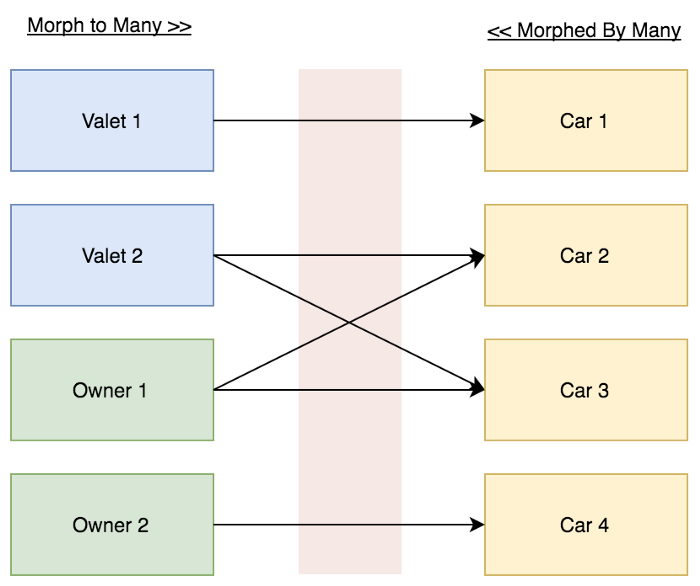
Details:
Trong ví dụ, chúng ta có 3 model (Valet, Owner & Car), 4 bảng (valets, owners, cars & drivers).
Business Rules:
- 1 người hầu trong nhà bạn - Valet có thể lái được nhiều loại xe ô tô trong nhà bạn - Cars.
- Bố bạn - Owner có thể lái được nhiều loại xe ô tô trong nhà - Cars.
- 1 chiếc xe ô tô - Car có thể được điều khiển bởi nhiều người lái xe - Valet / Owner.
Relations Diagrams:
Relationship Details:
Bảng trung gian - Pivot (drivers) phải lưu ID người lái xe (driver_id), người lái xe là ai - Valet/Owner (driver_type) và ID chiếc ô tô (car_id).
Eloquent Models:
class Valet
{
public function cars()
{
return $this->morphToMany(Car::class, 'driver');
}
}
class Owner
{
public function cars()
{
return $this->morphToMany(Car::class, 'driver');
}
}
class Car
{
public function valets()
{
return $this->morphedByMany(Valet::class, 'driver');
}
public function owners()
{
return $this->morphedByMany(Owner::class, 'driver');
}
}
Database Migrations:
Schema::create('valets', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->string('name');
});
Schema::create('owners', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->string('name');
});
Schema::create('drivers', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->integer('driver_id')->unsigned()->index();
$table->string('driver_type');
// or use $table->morphs(‘driver’); instead of "driver_id" and "driver_type"
$table->integer('car_id')->unsigned()->index();
$table->foreign('car_id')->references('id')->on('cars')->onDelete('cascade');
});
Store Records:
// Create relation between driver (Valet/Owner) and Car.
$valet->cars()->saveMany([$car1, $car2]);
$owner->cars()->saveMany([$car1, $car2]);
// Or use the save() function for single model.
$valet->cars()->save($car1);
$owner->cars()->save($car1);
// Create relation between Car and driver (Valet/Owner).
$car->valets()->attach([
$valet1->id,
$valet2->id,
]);
$car->owners()->attach([
$owner1->id,
$owner2->id,
]);
// Or use the sync() function to prevent duplicated relations.
$car->valets()->sync([
$valet1->id,
$valet2->id,
]);
$car->owners()->sync([
$owner1->id,
$owner2->id,
]);
Retrieve Records:
// Get driver (Valet/Owner) Cars
$valet->cars
$owner->cars
// Get Car drivers (Valet and Owner)
$car->owners
$car->valets
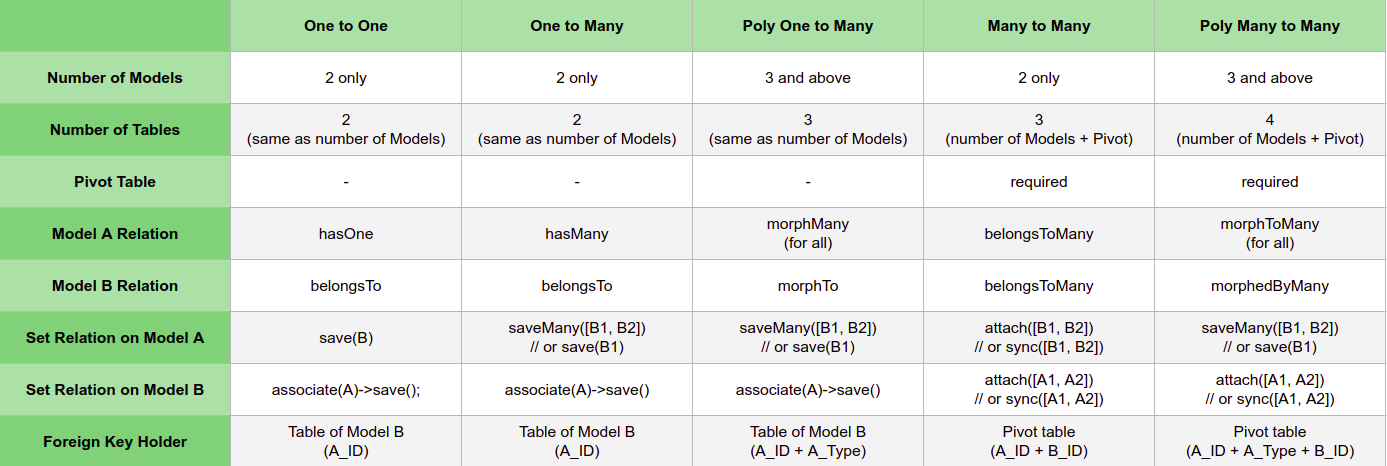
Tóm tắt
Tài liệu tham khảo
https://hackernoon.com/eloquent-relationships-cheat-sheet-5155498c209
All rights reserved